[This is a test site and all posts are generated with ChatGPT unless indicated otherwise.]
Keywords play a crucial role in Search Engine Optimization (SEO), acting as the bridge between what users search for and the content they find online. By strategically incorporating keywords into your website’s content, you can improve its visibility and attract organic traffic from search engines. When it comes to keywords, there are three main types: long tail, short tail, and medium tail.
Each type has its own unique characteristics, benefits, and considerations. In this article, we will explore the differences between long tail, short tail, and medium tail keywords, and provide insights on how to optimize your content effectively for each type. Let’s dive in!
1. Short Tail Keywords
Short tail keywords, also known as head terms or broad keywords, are brief and highly generic search phrases typically consisting of one or two words. These keywords have a high search volume and are often broad in nature, encompassing a wide range of topics. For instance, examples of short-tail keywords could include “shoes,” “digital marketing,” or “travel destinations.”

Characteristics of short tail keywords include:
- Broad Relevance: Short-tail keywords cover a wide range of topics and can be relevant to multiple industries or niches.
- High Search Volume: Due to their generic nature, short tail keywords tend to attract a large volume of search traffic.
- High Competition: Short tail keywords are highly competitive, as many websites target these popular search phrases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Short Tail Keywords
Advantages
- High Search Volume: Short tail keywords have a substantial search volume, which means there is a potential for significant traffic to your website.
- Brand Visibility: Targeting short tail keywords can increase your brand’s visibility and awareness among a broader audience.
Disadvantages
- Intense Competition: Since short tail keywords are highly competitive, it can be challenging to rank well in search engine results pages (SERPs) for these keywords.
- Vague User Intent: Due to their broad nature, short tail keywords often have unclear user intent. It becomes more difficult to gauge what users are specifically searching for, potentially leading to lower conversion rates.
Examples and Case Studies Illustrating the Use of Short Tail Keywords
- Example 1 – Clothing Retailer: A clothing retailer targeting the short tail keyword “shoes” might attract a large volume of traffic to their website. However, they may face tough competition from established brands and struggle to rank high in SERPs.
- Case Study – Digital Marketing Agency: A digital marketing agency targeting the short tail keyword “digital marketing” could potentially generate a significant amount of website traffic. However, due to the highly competitive nature of this keyword, it would require a comprehensive and effective SEO strategy to stand out from the competition.
Tips for Optimizing Content with Short Tail Keywords
- Focus on Relevance: Even though short tail keywords are broad, ensure that your content remains relevant to the keyword. Include high-quality and informative content that satisfies user intent.
- Create Compelling Titles and Meta Descriptions: Craft compelling and attention-grabbing titles and meta descriptions that entice users to click on your search result amidst fierce competition.
- Optimize On-Page Elements: Incorporate short tail keywords strategically in your page’s headings, subheadings, and body text, while ensuring the content remains natural and readable.
- Use Long-Form Content: Develop comprehensive, in-depth content around short tail keywords to increase your chances of ranking higher in SERPs.
- Utilize Paid Advertising: Consider using paid advertising options like Google Ads to supplement your SEO efforts and increase visibility for short tail keywords.
Remember, while short tail keywords can attract significant traffic, it’s important to carefully balance their use with other types of keywords to ensure a well-rounded SEO strategy.
By understanding the unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of short tail keywords, you can optimize your content effectively to improve search engine visibility and drive relevant traffic to your website.
2. Long Tail Keywords
Long tail keywords are longer, more specific search phrases that consist of three or more words. Unlike short tail keywords, long tail keywords are highly targeted and narrow in focus. For example, long tail keywords could include phrases like “best running shoes for women with flat feet” or “affordable family vacation destinations in Europe.”

Characteristics of long tail keywords include:
- Specificity: Long tail keywords target a particular niche, addressing specific user intent or query.
- Lower Search Volume: Long tail keywords have lower search volume compared to short tail keywords, but they often have higher conversion rates.
- Lower Competition: Due to their specific nature, long tail keywords typically have lower competition, making it easier to rank higher in SERPs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Long Tail Keywords
Advantages
- Higher Conversion Rates: Long tail keywords attract users with clear intent, resulting in higher conversion rates and more targeted traffic.
- Lower Competition: With lower competition, it is relatively easier to rank higher in SERPs for long tail keywords, giving you an opportunity to gain visibility and establish authority in specific niches.
Disadvantages
- Lower Search Volume: Long tail keywords have lower search volume compared to short tail keywords, which means the potential for traffic may be limited.
- Limited Scale: Due to their specificity, focusing solely on long tail keywords may restrict your ability to reach a broader audience.
Examples and Case Studies Illustrating the Use of Long Tail Keywords
- Example 1 – Home Improvement Blog: A home improvement blog targeting the long tail keyword “how to install laminate flooring in a small bathroom” may attract fewer overall searches but has a higher chance of reaching users specifically looking for that information. This targeted approach can result in more engaged and satisfied readers.
- Case Study – Recipe Website: A recipe website targeting the long tail keyword “easy gluten-free vegan chocolate chip cookies” might face less competition than if they were targeting a broader keyword like “chocolate chip cookies.” This focused approach can help them attract a specific audience interested in gluten-free and vegan recipes.
Tips for Optimizing Content with Long Tail Keywords
- Keyword Research: Conduct thorough keyword research to identify relevant long tail keywords that align with your content and target audience. Utilize tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to discover long tail keyword opportunities.
- Content Creation: Develop high-quality, informative content that addresses the specific user intent of the long tail keyword. Provide detailed answers and solutions to the user’s query.
- Include Long Tail Keywords Naturally: Incorporate long tail keywords organically throughout your content, including in headings, subheadings, body text, and meta tags. However, ensure that the content reads naturally and doesn’t appear forced or spammy.
- Answer Questions: Long tail keywords often contain question phrases. Address these questions directly within your content to cater to users seeking specific information.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your long tail keyword-optimized content. Analyze metrics such as organic traffic, engagement, and conversions to evaluate the effectiveness of your strategy and make necessary adjustments.
By leveraging the specificity and targeting power of long tail keywords, you can attract highly relevant traffic, improve conversion rates, and establish your website’s authority in specific niches.
3. Medium Tail Keywords
Medium tail keywords are search phrases that fall between short tail and long tail keywords in terms of length and specificity. They typically consist of two to three words and offer a moderate level of specificity. Medium tail keywords strike a balance between broad and highly targeted search terms. Examples of medium tail keywords include “best digital cameras” or “social media marketing tips.”
Characteristics of medium tail keywords include:
- Moderate Specificity: Medium tail keywords provide a moderate level of specificity, targeting a narrower audience compared to short tail keywords.
- Moderate Competition: Medium tail keywords have a moderate level of competition, falling between the highly competitive short tail keywords and the less competitive long tail keywords.
- Balanced Search Volume: Medium tail keywords generally have a decent search volume, allowing for a good balance between attracting traffic and maintaining relevance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Medium Tail Keywords
Advantages
- Balanced Competition: Medium tail keywords offer a balance between targeting a specific audience and facing moderate competition. This can increase your chances of ranking higher in SERPs compared to short tail keywords.
- Higher Relevance: Medium tail keywords allow you to reach a more targeted audience with clear intent, resulting in better user engagement and conversion rates.
Disadvantages
- Moderate Search Volume: Medium tail keywords may have a lower search volume compared to short tail keywords, which can limit the overall traffic potential.
- Less Specific: While medium tail keywords provide a certain level of specificity, they may not address highly specific queries or niche topics as effectively as long tail keywords.
Examples and Case Studies Illustrating the Use of Medium Tail Keywords
- Example 1 – Fitness Blog: A fitness blog targeting the medium tail keyword “best home workout equipment” can attract an audience interested in purchasing workout equipment for home use. This medium tail keyword strikes a balance between specificity and search volume.
- Case Study – Travel Agency: A travel agency targeting the medium tail keyword “affordable beach resorts in Southeast Asia” may attract users who are looking for budget-friendly beach resorts in that specific region. This medium tail keyword allows the agency to target a specific audience while still having a decent search volume.
Tips for Optimizing Content with Medium Tail Keywords
- Understand User Intent: Research and understand the user intent behind medium tail keywords. Tailor your content to address the specific needs, questions, or desires of the target audience.
- Create Informative Content: Develop comprehensive and informative content that provides valuable insights, tips, or solutions related to the medium tail keyword. This helps establish your authority in the subject matter and improves user engagement.
- Use in Headings and Subheadings: Incorporate medium tail keywords naturally in your headings, subheadings, and content sections. This helps search engines understand the relevance of your content and improves visibility.
- Focus on Long-Form Content: Consider creating long-form content around medium tail keywords to provide in-depth information and satisfy user intent.
- Leverage Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI): Include related terms and synonyms within your content to signal to search engines the comprehensive coverage of the topic and increase the chances of ranking for related queries.
Medium tail keywords offer a balanced approach, allowing you to target a specific audience while still maintaining a reasonable search volume. By optimizing your content effectively around medium tail keywords, you can attract relevant traffic and improve your website’s visibility.
Key Differences between Long, Short, and Medium Tail Keywords
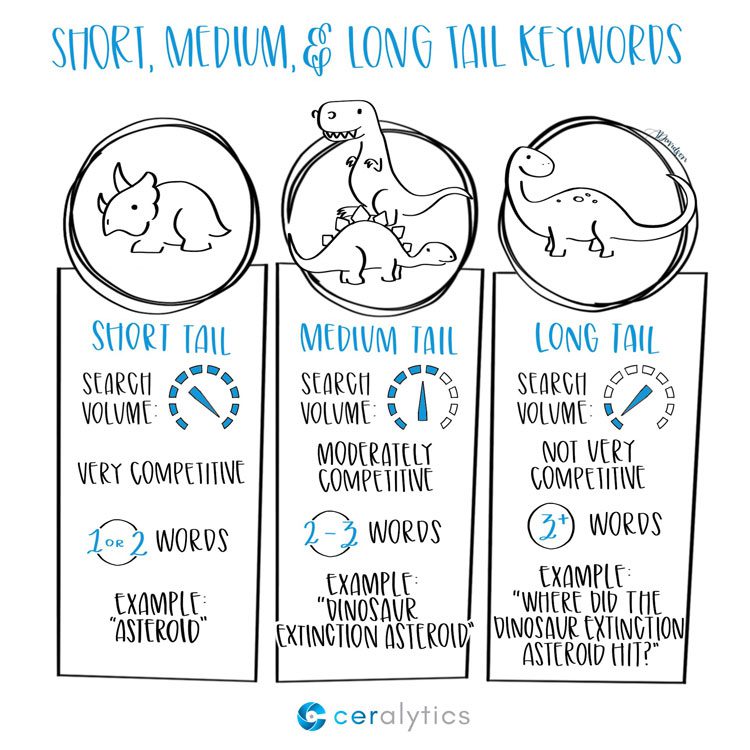
1. Search Volume and Competition
- Short Tail Keywords: Short tail keywords have high search volumes due to their broad nature, attracting a large number of searches. However, they also face intense competition, making it challenging to rank well in SERPs.
- Medium Tail Keywords: Medium tail keywords have a moderate search volume. While they may not attract as much traffic as short tail keywords, they often face less competition, providing better opportunities to rank higher in search results.
- Long Tail Keywords: Long tail keywords have lower search volumes compared to short and medium tail keywords. However, they also have significantly less competition, allowing for easier ranking in SERPs.
2. User Intent and Specificity
- Short Tail Keywords: Short tail keywords are broad and often lack clear user intent. Users searching with short tail keywords may have varied intentions, making it more challenging to tailor content specifically to their needs.
- Medium Tail Keywords: Medium tail keywords offer a moderate level of specificity, allowing you to target a more defined audience with clearer intent. Users searching with medium tail keywords generally have a specific topic or product in mind.
- Long Tail Keywords: Long tail keywords are highly specific and indicate a clear user intent. Users searching with long tail keywords typically have a specific question, problem, or niche interest, allowing you to deliver highly relevant content.
3. Conversion Potential and Relevance
- Short Tail Keywords: Short tail keywords may attract high traffic, but their conversion potential can be lower due to vague user intent. The broad nature of these keywords can result in a mix of relevant and irrelevant traffic.
- Medium Tail Keywords: Medium tail keywords strike a balance between relevance and search volume. They attract a more targeted audience, resulting in higher conversion potential compared to short tail keywords.
- Long Tail Keywords: Long tail keywords have the highest conversion potential. Users searching with long tail keywords are often seeking specific solutions or information, indicating a strong intent to take action.
4. Target Audience and Niche Targeting
- Short Tail Keywords: Short tail keywords have a broad target audience, as they cater to a wide range of interests and industries. It can be challenging to narrow down the target audience with these keywords alone.
- Medium Tail Keywords: Medium tail keywords allow for better niche targeting. By focusing on specific topics or products, you can attract a more defined audience interested in those particular areas.
- Long Tail Keywords: Long tail keywords enable precise niche targeting. By addressing highly specific queries, you can reach a smaller but highly relevant and engaged audience interested in a particular niche or topic.
Understanding these key differences between long, short, and medium tail keywords is crucial for developing an effective keyword strategy. By considering factors like search volume, competition, user intent, conversion potential, and target audience, you can optimize your content to attract the right audience, increase relevance, and achieve your desired goals.
Choosing the Right Keyword Strategy

1. Understanding Your Goals and Objectives
- Define Your Goals: Determine the purpose of your website or content. Are you looking to drive traffic, generate leads, increase sales, or establish thought leadership? Clarifying your goals will help shape your keyword strategy.
- Identify your Target Audience: Understand your target audience’s preferences, needs, and search behaviors. This will help you choose keywords that align with their interests and improve the relevance of your content.
2. Analyzing Keyword Research and Competitor Analysis
- Keyword Research: Conduct thorough keyword research using tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs. Identify relevant keywords with a balance of search volume, competition, and relevance to your content or offerings.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze the keyword strategies of your competitors. Identify the keywords they are targeting, their search rankings, and the gaps you can leverage to differentiate yourself.
3. Balancing Short, Medium, and Long Tail Keywords for Optimal Results
- Short Tail Keywords: Short tail keywords help attract high search volume but come with intense competition. Use them sparingly and focus on high-value, highly relevant short tail keywords to improve visibility and brand awareness.
- Medium Tail Keywords: Medium tail keywords strike a balance between search volume and specificity. They offer better targeting opportunities and can help you attract a more relevant audience.
- Long Tail Keywords: Long tail keywords provide highly specific targeting and often have less competition. They offer opportunities to capture highly engaged users seeking specific information, leading to higher conversion rates.
4. Tools and Techniques for Effective Keyword Research
- Keyword Research Tools: Utilize keyword research tools such as Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to discover relevant keywords, analyze search volumes, and identify keyword trends.
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Engage with your audience through surveys or feedback forms to understand the language they use when searching for information related to your products or services.
- Google Trends: Monitor Google Trends to identify popular topics and seasonal trends. This can help you align your content strategy with trending keywords.
- Long-Form Content and FAQs: Create comprehensive, long-form content that addresses user questions and includes relevant long tail keywords. This approach can increase visibility and cater to specific user intent.
- Semantic SEO: Leverage semantic SEO techniques by incorporating related terms and synonyms in your content. This helps search engines understand the context and relevance of your content.
Remember, a successful keyword strategy requires continuous monitoring and refinement. Regularly analyze your website’s performance, track keyword rankings, and make adjustments based on user behavior and market trends. By choosing the right mix of keywords and staying attuned to your goals, you can optimize your content for search engines, attract the right audience, and achieve your desired outcomes.
Best Practices for Keyword Optimization
1. On-Page Optimization Techniques
- Title Tags: Optimize your title tags by including your target keyword at the beginning and making them compelling and concise.
- Meta Descriptions: Craft meta descriptions that entice users to click while incorporating relevant keywords naturally.
- URL Structure: Ensure your URL structure is clean, concise, and includes your target keyword when appropriate.
- Header Tags: Use header tags (H1, H2, etc.) to organize your content and incorporate keywords in a logical and natural way.
- Keyword Placement: Strategically place keywords in the content body, ensuring they flow naturally and do not appear forced or spammy.
- Image Optimization: Optimize images by using descriptive file names and alt tags that include relevant keywords.
2. Creating High-Quality and Engaging Content around Keywords
- Content Relevance: Develop content that aligns with user intent and addresses their needs and queries. Ensure it is informative, valuable, and relevant to the keywords you are targeting.
- Keyword Density: Aim for a natural keyword density throughout your content. Avoid overstuffing keywords, as it can negatively impact user experience and search engine rankings.
- Variations and Synonyms: Incorporate variations and synonyms of your target keywords to enhance the semantic relevance of your content.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Provide comprehensive coverage of the topic to demonstrate expertise and satisfy user intent. This can include addressing related subtopics and answering common questions.
- User Engagement: Create content that encourages user engagement, such as incorporating multimedia elements, interactive features, and opportunities for social sharing and comments.
3. Monitoring and Tracking Keyword Performance
- Analytics Tools: Utilize tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to track keyword rankings, organic traffic, and user engagement metrics.
- Ranking Reports: Regularly monitor your keyword rankings to identify improvements, opportunities, and areas that may require optimization.
- User Behavior Analysis: Analyze user behavior metrics, such as bounce rate, time on page, and conversion rates, to understand the effectiveness of your keyword optimization efforts.
4. Adapting to Changes in Search Engine Algorithms
- Stay Updated: Stay informed about the latest changes and updates in search engine algorithms through reputable industry sources and blogs.
- Quality Guidelines: Adhere to search engine quality guidelines to ensure your content remains compliant and relevant.
- Continuous Optimization: Continuously evaluate and adapt your keyword strategy based on algorithm updates, user behavior, and keyword performance metrics.
- Diversify Your Strategy: Focus on building a robust and diversified content strategy that incorporates various optimization techniques beyond keyword usage, such as improving site speed, enhancing user experience, and gaining quality backlinks.
Remember, keyword optimization is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring, analysis, and adaptation. By following these best practices, you can optimize your content effectively, improve search engine visibility, attract the right audience, and drive meaningful results for your website or business.
Long vs Medium vs Short tail keywords: Which is Best for Your Brand?
In this comprehensive guide, we explored the differences between long, short, and medium tail keywords and delved into the best practices for keyword optimization. Let’s recap the key points discussed:
- Long tail keywords are highly specific, while short tail keywords are broad. Medium tail keywords strike a balance between the two.
- Each type of keyword has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of search volume, competition, and user intent.
- Choosing the right keyword strategy involves understanding your goals, conducting thorough research, and finding a balance between short, medium, and long tail keywords.
- On-page optimization, high-quality content creation, monitoring keyword performance, and adapting to search engine algorithm changes are crucial for successful keyword optimization.
It cannot be emphasized enough how important it is to choose the right keyword strategy. The right keywords can make a significant impact on your search engine rankings, organic traffic, user engagement, and ultimately, your business goals. A well-crafted keyword strategy helps you reach the right audience, increase relevance, and drive meaningful results.
As you embark on your keyword optimization journey, remember to experiment and refine your techniques. Continuously monitor keyword performance, adapt to algorithm changes, and stay up-to-date with industry trends. By testing and iterating, you can uncover new insights, improve your optimization efforts, and achieve better results over time.
Now, it’s time to put your knowledge into action. Start implementing these best practices, analyze your keyword performance, and refine your strategy based on the insights gained. With a well-executed keyword optimization approach, you can enhance your website’s visibility, attract the right audience, and pave the way for online success.

